Leveraging Open RAN To Build Networks Of The Future - Ramin Attari, Regional VP Sales - Middle East And Africa, Parallel Wireless

Over the last 18 months, Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) in Africa played a stellar role in pivoting to meet the new and evolving telecommunication needs. They rose to the occasion to ensure people could carry out their professional and personal tasks even as social distancing norms and stay-at-home restrictions turned the world upside down.
Even so, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed the digital divide in Africa. With only 33% of Africans using the internet , and only 51% of the population covered by 4G in sub-Saharan Africa, the unconnected were unable to benefit from telecommuting, e-commerce, online learning, and e-health. The pandemic has highlighted that universal connectivity to quality high-speed broadband is crucial to building economic resilience in the wake of the growing digital economy.
In essence, the MNOs have to address two very diverse requirements of the customers in Africa. Even as 4G and 5G are being deployed in some regions, the African market is still heavily dependent on 2G and 3G. Essentially this means that the MNOs need to support several technologies, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G, for a long time leading to network complexity and an increase in CAPEX and OPEX.
Making sense of the RAN economics
The Radio Access Network (RAN) economy plays a crucial role in deciding the overall strategy for the MNO and is largely to blame for their urban-focused go-to-market business strategy. Expenditure on RAN constitutes 60 to 80% of the overall network expense for an MNO. Typically, the service providers have ignored the rural areas because setting up a network in remote areas is expensive and offers a low Return On Investment (ROI) spread over a longer period of time.
Fortunately, the African MNOs are exploring new solutions to provide high-speed and low-cost connectivity in rural and remote areas. This is also driven by the need to move from costly, proprietary RAN solutions from legacy providers to Open RAN with Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) and software-based architecture.
Open RAN is emerging as a technology approach of choice to empower MNOs to add new capabilities while bringing down CAPEX to deploy the network in yet-to-be-connected areas. Furthermore, since Open RAN is software-driven, it also allows MNOs to effectively manage existing technologies such as 2G and 3G while introducing new technologies, such as 4G and 5G.
Using Open RAN to address market challenges
In simple terms, Open RAN brings down the RAN expense for an MNO by reducing its dependence on expensive proprietary hardware and software. MTN , Hotspot and Orange are some of the African service providers that have already started to benefit from Open RAN.
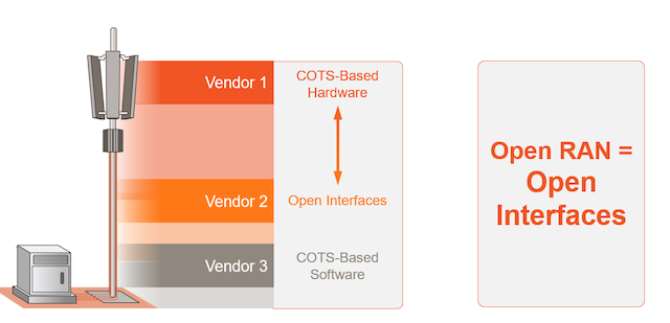
The Open RAN movement started with the cloud RAN (cRAN) initiative about a decade earlier. This was followed by virtual RAN (vRAN), in which the Baseband Unit (BBU) is replaced by a COTS server instead of proprietary hardware. Today, Open RAN is about using vendor-neutral hardware and software-defined technology with open, non-proprietary interfaces. By disaggregating the hardware and software components of the network, Open RAN enables MNOs to use BBUs, radio units, remote radio heads and software from different vendors without facing any interoperability issues. Furthermore, only software upgrades are required, making it easier and more cost-effective for MNOs to modernize their networks.
Cloud-native, software-enabled Open RAN is helping MNOs bring down the cost of setting up, managing and upgrading networks. Since the traditional RAN platforms are based on proprietary hardware, MNOs are dependent on the vendor for innovations, which leads to significant additional investment from the operator every time there is an upgrade. This means that the MNOs need to work with the same vendor for both hardware and software. There is little option to move from one vendor to another because they would need to change all components of the entire network. This is not the case with Open RAN, where MNOs can modernize their networks as needed and when required. With Open RAN, the MNOs are much more in control of their networks.
Even as the 5G footprint expands in Africa, 2G and 3G will continue to remain relevant for several years to come. However, 2G in its present form is not geared to address the evolving needs of the end-user. Open RAN, which leverages the principles of virtualization, can help the MNOs address this dichotomy and enable a smooth upgrade to 5G whenever the market is ready.
It is then hardly surprising that the Open RAN ecosystem continues to move from strong to stronger. The Open RAN market is likely to exceed the traditional RAN market for the first time by 2027-28, according to ABI Research . Open RAN is not just about changes in the network architecture. It allows MNOs to address the market challenges while accelerating innovation and setting the base for new business models.
Reimagining the Networks
With such widespread benefits, Open RAN has disrupted the market and is redefining how networks are designed and managed in Africa. It allows MNOs to bring down the cost associated with RAN while making it easier to address newer markets cost-effectively. Further, it frees the service providers to go beyond legacy vendors to opt for products and solutions most suited to their requirements without worrying about interoperability.
The traditional network architecture is not designed to address the needs of rural requirements. The last few months have demonstrated that quality broadband is fundamental to overall economic and social growth. The pandemic has made it imperative for the MNOs to reimagine their networks to extend the benefit of the internet to everyone, even those in rural areas. The Open RAN approach addresses the pain points of the MNOs and empowers them to gain new customers by cost-effectively expanding the network in remote and rural areas.
Open RAN networks are here to stay and are the future of wireless networks. The concept allows MNOs to drive cost efficiencies while enabling them to provide innovation and broadband connectivity to the yet-to-be-connected, thus enhancing lives and boosting economies.